

Great white sharks, like many other sharks, have rows of serrated teeth behind the main ones, ready to replace any that break off. From above, the darker shade blends with the sea and from below it exposes a minimal silhouette against the sunlight. The coloration makes it difficult for prey to spot the shark because it breaks up the shark's outline when seen from the side. Great whites display countershading, having a white underside and a grey dorsal area (sometimes in a brown or blue shade) that gives an overall mottled appearance.
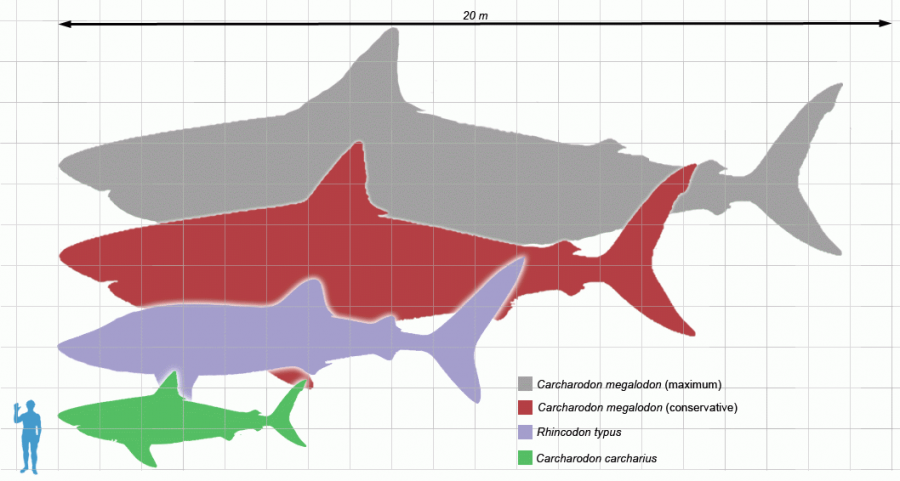
The upper and lower lobes on the tail fin are approximately the same size (like some mackerel sharks). The great white shark has a robust large conical snout. Possibilities include seasonal feeding or mating. Why they migrate and what they do at their destination is still unknown. This refuted traditional theories that white sharks are coastal territorial predators and opens up the possibility of interaction between shark populations that were previously thought to be discrete. Another white shark tagged off the South African coast swam to the southern coast of Australia and back within the year. After they arrive, they change behavior and do short dives to about 300 m (1,000 ft) for up to 10 minutes. On the journey out, they swim slowly and dive down to around 900 m (3,000 ft). According to a recent study, California great whites have migrated to an area between Baja California and Hawaii known as White Shark Café to spend at least 100 days before migrating back to Baja. These findings challenge the traditional notion about the great white as being a coastal species. In the open ocean it has been recorded at depths as great as 1,220 m (4,000 ft). It is an epipelagic fish, observed mostly in the presence of rich game like fur seals, sea lions, cetaceans, other sharks, and large bony fish species. One of the densest known populations is found around Dyer Island, South Africa where much shark research is conducted. Great white sharks live in almost all coastal and offshore waters which have water temperature between 12 and 24 ☌ (54 and 75 ☏), with greater concentrations in the United States (Atlantic Northeast and California), South Africa, Japan, Australia (especially New South Wales and South Australia), New Zealand, Chile, and the Mediterranean. The IUCN treats the great white shark as vulnerable, while it is included in Appendix II of CITES. It is the only known surviving species of its genus, Carcharodon, and is ranked first in a list of number of recorded attacks on humans. It is also known to prey upon a variety of other marine animals including fish, pinnipeds, and seabirds. The great white shark is arguably the world's largest known extant macropredatory fish and is one of the primary predators of marine mammals. This shark reaches maturity at around 15 years of age and can have a life span of over 30 years. It is known for its size, with the largest individuals known to have approached or exceeded 6 metres (20 ft) in length, and 2,268 kilograms (5,000 lb) in weight. The great white shark, scientific name Carcharodon carcharias, also known as the great white, white pointer, white shark, or white death, is a large lamniform shark found in coastal surface waters in all major oceans. Great White Shark - Carcharodon carcharias cerrejonensis reached a maximum length of 12 to 15 m (40 to 50 ft), weighed about 1,135 kg (2,500 lb), and measured about 1 m (3 ft) in diameter at the thickest part of the body. By comparing the sizes and shapes of its fossilized vertebrae to those of extant snakes, researchers estimated T. The only known species is the Titanoboa cerrejonensis, the largest snake ever discovered, which supplanted the previous record holder, Gigantophis. Titanoboa, /taɪˌtænəˈboʊ.ə/ ty-tan-ə-boh-ə meaning "titanic boa," is a genus of snake that lived approximately 58–60 million years ago, during the Paleocene epoch, a 10-million-year period immediately following the dinosaur extinction event.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
